Servo Motor has an advantage over normal DC motor because it can move shaft very precisely even at a particular angle. It is very useful in embedded and electronics applications for controlling the robotic arm, sensor or moving object connected to its shaft at a certain angle. It has integrated gears and circuit that providing feedback system.
In this tutorial, an RC hobby servo is directly connected to the arduino board. Servo motor current consumption is very high so some time arduino can’t drive it. A standard servo can be positioned at a different angle from 0 to 180 degree. We can move the servo at a particular angle by doing the servo programming.
Table of Contents
Servo PWM
Servo has a PWM pin. So by applying the pulse of +5V usually between 1ms to 2ms repeated at around 20ms. Servo gets the position from 0 to 180 degrees.

| PWM | Degree |
|---|---|
| 1ms | 0 |
| 1.5ms | 90 |
| 2ms | 180 |
Servo Pinout

Servo has three wire:
- GND
- Vcc(+5V)
- PWM
Here in this hobby servo, we have a brown wire for GND, red for Vcc and orange for PWM.
Hardware Required
- Arduino Uno
- Servo 9G
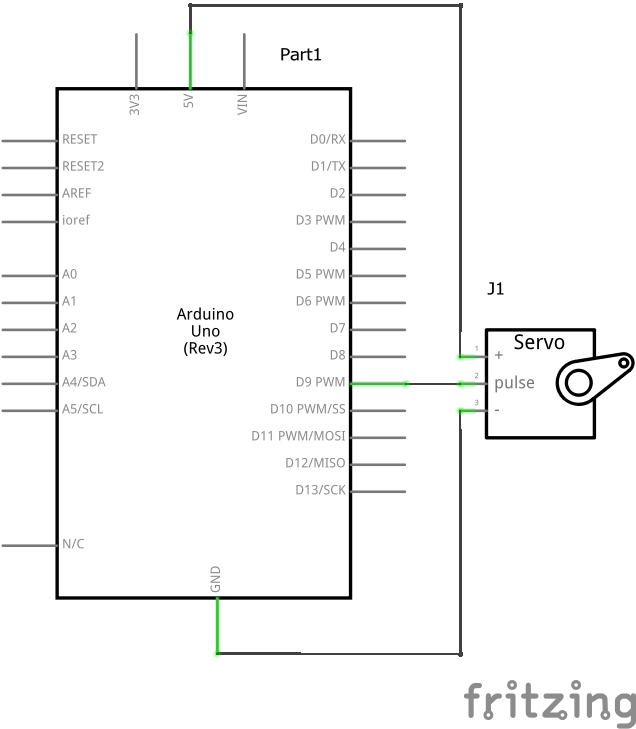
Arduino Servo Motor Connection
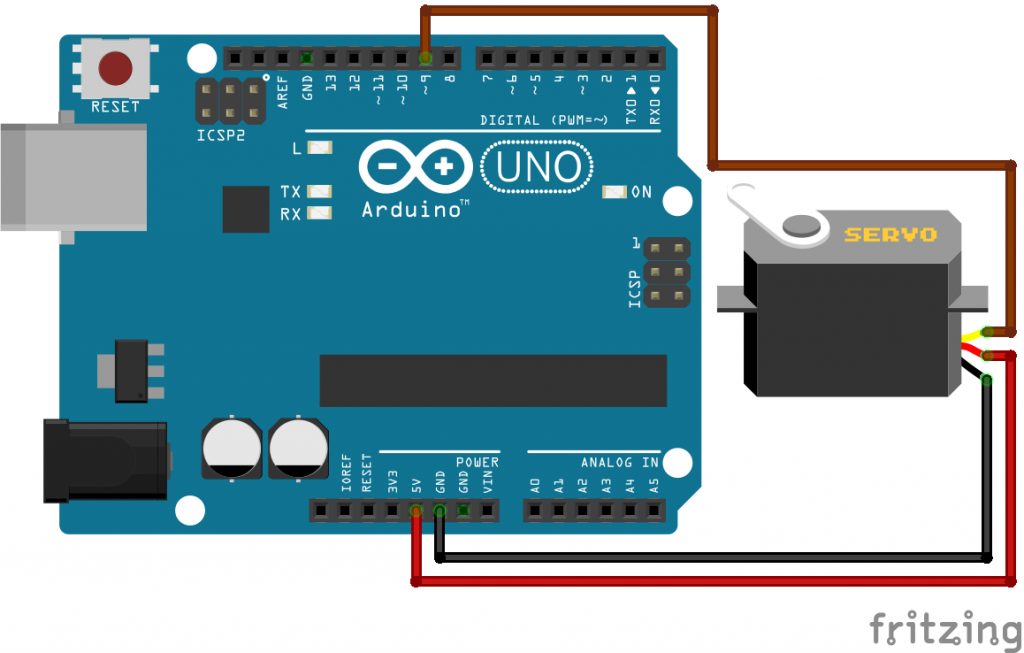
Arduino Servo Motor Circuit
Servo Library
We are using ardunio servo library, so controlling servo is very easy. Arduino library supports up to 12 servos on the most arduino board. Servo Library has following functions:
- attach()Attach servo variable to arduino pin.
Syntaxservo.attach(pin) - write()Control the servo by using the function
servo.write(angle). We can move the servo shaft at desired angle. - writeMicroseconds()Write the value in uS to function to control
servo.writeMicroseconds(uS)the angle of servo shaft. A value of 1000 means counter-clockwise, 2000 is fully clockwise, and 1500 is in the middle position of the shaft. - read()Read the current angle of the servo using the function
servo.read(). - attached()Check whether servo variable is connected to the arduino pin. Function
servo.attached()return true if connected else false. - detach()Function
servo.detach(),detach the servo variable from the arduino pin. And now these pin 9,10 can be used as PWM pin.
Arduino Servo Code
In servo library you will get these two programs:
Knob: Control the position of a servo with a potentiometer.
// Controlling a servo position using a potentiometer (variable resistor)// by Michal Rinott <http://people.interaction-ivrea.it/m.rinott> #include <Servo.h> Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin void setup() { myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object } void loop() { val = analogRead(potpin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023) val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 179); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180) myservo.write(val); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value delay(15); // waits for the servo to get there }
Sweep: Sweep the shaft of a servo motor back and forth.
// Sweep// by BARRAGAN <http://barraganstudio.com> // This example code is in the public domain. #include <Servo.h> Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo // a maximum of eight servo objects can be created int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position void setup() { myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object } void loop() { for(pos = 0; pos < 180; pos += 1) // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees { // in steps of 1 degree myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos' delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position } for(pos = 180; pos>=1; pos-=1) // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees { myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos' delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position } }